Building Digital Media Literacy with Wiseone's cross-check

Introduction
Nowadays, the omnipresence of digital media is undeniable. From the screens of our smartphones to the billboards towering over city streets, digital media has permeated every aspect of our lives.
Digital media literacy is essential in the Information Age as we navigate this digital landscape. Equipping individuals with the ability to critically analyze, comprehend, and effectively engage with the digital content we encounter daily is becoming necessary.
The following article discusses digital media literacy, shedding light on its meaning, significance, and challenges and exploring its various facets. The role of Wiseone's Cross-Check is a pioneering feature dedicated to tackling digital media literacy by providing easy access to diverse perspectives.
The Digital Media Landscape
The current digital media landscape
The current state of the digital media landscape is dynamic and transformative, shaping how individuals interact, consume, and disseminate information. With the Internet and the proliferation of social media platforms, digital media has become a primary source of news, entertainment, and communication for billions of people worldwide.
The democratization of information dissemination has brought immense benefits. However, significant challenges have been raised, too.
One of the most pressing issues is the proliferation of misinformation and fake news that can spread like wildfire in the digital realm, fueled by the rapidity with which information is shared and the echo chambers that often reinforce false narratives.
This phenomenon deteriorates trust in traditional media and seriously threatens the fabric of democratic societies.
Social media in the news
Social media firms have been in the news lately, not always for good reasons. The common problems surrounding them include controversy over user privacy and online safety.
- Facebook/Meta
Facebook rebranded as Meta in 2021 to focus on the metaverse. However, it lost billions in R&D money as the metaverse didn't take off as originally planned. Meta has announced that it's now focusing on AI applications.
In 2022, Facebook and its subsidiary Instagram began losing subscribers as younger generations moved to apps such as TikTok and YouTube.
Facebook has been repeatedly cited for user privacy violations and fined $5 billion by the European Union.
- Snapchat
Snapchat recently introduced augmented reality (AR) to its application, including a new method for creating custom AR lenses and a new way to share AR experiences with friends. Users can now create their AR lenses using various tools and assets, which they canshare with friends.
In 2021, Snapchat partnered with Disney to create an AR experience. This includes new ways to interact with Disney characters and watch Disney movies. It also introduced a new subscription service – Snapchat+ – with several exclusive features, such as seeing who has rewatched snaps and access to a particular chat feature to video chat and call other users from the platform.
But Snapchat is facing the challenge of declining user growth, most notably due to competition from the giant TikTok.
- TikTok
TikTok has emerged as a popular platform for video blogging. However, its success is filled with controversy, the most notable being that the parent company of TikTok, ByteDance, might have connections to the Chinese Communist Party.
ByteDance has been accused of collecting and storing user data for the Chinese government. It has also been accused of being a national security risk that spies on American users. Nothing concrete has been found; the accusations mainly stem from the ambiguity of the software's privacy statement.
TikTok has also been criticized for allowing harmful content – such as cyberbullying and self-harm videos – that targets minors to be shared on the platform. TikTok has taken steps to address this issue, but it remains a concern.
Twitter has faced turbulent times since Elon Musk took over in 2022. Under Musk's leadership, Twitter has seen changes to its platform that some consider damaging, such as cutting content moderation staff and loosening moderation rules. Users scrambled for Twitter alternatives, and advertisers suspended or canceled ad buys.
Many startups have attempted to capitalize on user dissatisfaction – including the right-wing leaning Gab and the techie-oriented Mastodon – but none have gained any real traction. Jack Dorsey, one of the founders of Twitter, started Bluesky, which is similar to Twitter but is currently in beta testing for only those with invites.
Musk named Linda Yaccarino, former head of advertising at NBCUniversal, Twitter's new CEO in 2023. She will face the challenge of regaining advertiser confidence to boost the company's revenue.
Understanding Digital Media Literacy
Digital media literacy is a crucial skill set that empowers individuals to navigate information with discernment and confidence.
At its core, digital media literacy holds a multifaceted approach to engaging with digital content. It involves the development of critical thinking, enabling individuals to question, analyze, and interpret the information they read online.
Media analysis is another integral component, encouraging individuals to deconstruct the messages, narratives, and biases embedded within various forms of digital media.
Digital media literacy's significance extends beyond personal empowerment; it plays a vital role in shaping informed individuals. It equips them to participate meaningfully in public discourse, make informed decisions, and contribute positively to society.
Also, digital media literacy fosters a sense of agency, transforming passive consumers into active creators and collaborators.
Confirmation Bias in Digital Media
Confirmation bias, a cognitive phenomenon deeply embedded in human psychology, profoundly influences digital media consumption.
This bias refers to the tendency of individuals to seek, interpret, and remember information in a way that confirms their preexisting beliefs and values while actively avoiding or dismissing information that contradicts them.
In digital media, confirmation bias can operate surreptitiously, leading individuals to selectively engage with content that aligns with their worldviews. This can manifest in various ways, such as following news outlets or social media accounts that echo their perspectives while unfollowing or dismissing those with differing viewpoints.
Confirmation bias in the digital media landscape can reinforce existing misinformation and prejudices, creating self-reinforcing echo chambers where individuals are exposed only to content that confirms their biases.
For instance, in online political communities, users may be more likely to share and engage with news articles or social media posts that validate their political beliefs, regardless of their accuracy.
This can rapidly spread false or misleading information within these closed circles, further entrenching individuals in their preconceived notions. In this section, we will explore the insidious nature of confirmation bias in digital media consumption and delve into its detrimental effects on information accuracy and the polarization of online communities.
Challenges in Building Digital Media Literacy
While building digital media literacy is crucial in today's information-driven society, it has its challenges and obstacles.
- One of the primary challenges individuals may encounter is the overwhelming volume of digital content and information available, which can be intimidating, making it difficult to discern what's reliable and what's not.
- Additionally, confirmation bias, as discussed earlier, can be a formidable obstacle, as people often gravitate toward information confirming their existing beliefs, inadvertently reinforcing their prejudices.
- Furthermore, the rapid evolution of digital technologies and media platforms can make it challenging to keep up with the latest trends and tools for media literacy.
However, these challenges can be overcome with the right approach.
- Developing critical thinking skills is essential in evaluating digital content.
- Fact-checking and cross-referencing information from multiple sources can help individuals filter out misinformation.
- Engaging with diverse perspectives and being open to different viewpoints can counter confirmation bias.
- Taking advantage of dedicated tech tools.
Introduction to Wiseone's Cross-Check
What is Cross-check?
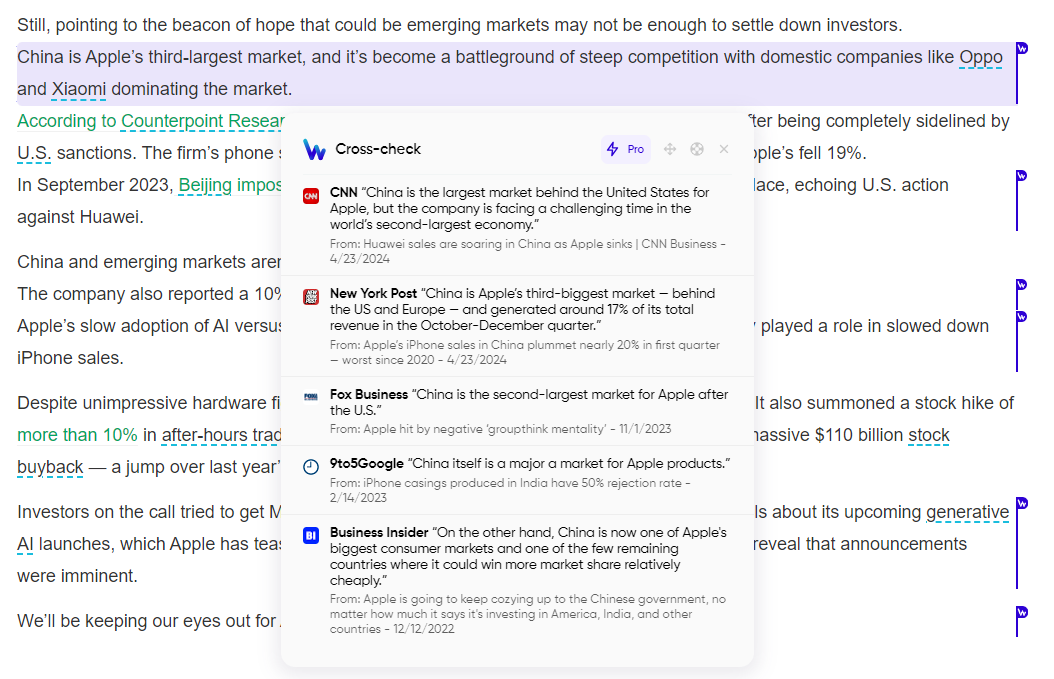
The relentless surge of online content and the increase of misinformation present a significant challenge to individuals striving to navigate this landscape effectively.
Wiseone's Cross-Check is a feature designed to help individuals with the means to assess information. The innovative tool simplifies access to a curated selection of factual and dependable sources covering the same topic.
It is a valuable resource in the digital era, allowing users to verify information and gain a more comprehensive and impartial perspective.
Using Wiseone's Cross-Check
Understanding how to make the most of Wiseone's Cross-Check is an easy process that can significantly enhance digital media literacy.
To use Cross-Check effectively, follow these simple steps:
- Identify the Dark Blue Line: While reading an article, look for a paragraph or sentence marked with a dark blue line on the article's left margin. This is your cue that Wiseone's Cross-Check is ready to assist.
- Hover or Click for Information: Hover your mouse cursor over the marked paragraph or sentence to click on it. A pop-up window will appear.
- List Relevant Articles: Within the pop-up window, you'll find a space to list the most pertinent articles related to the fact or information in question. This step allows you to access a curated selection of pieces that offer diverse perspectives and reliable information on the same subject matter.
Whether fact-checking a news story, researching a contentious topic, or seeking a more comprehensive understanding of a given subject, Wiseone's Cross-Check helps you to navigate the digital landscape confidently and precisely.
How to get Cross-check
Getting started with Wiseone is easy. Follow these simple steps to boost your reading productivity and your online search experience:
Download and Install: Visit the Chrome Web Store, download the Wiseone extension, and create an account.
Pin the Extension: Once installed, pin the extension to your browser for easy access to its features.
Enable the Extension: Click "enable Wiseone," and a quick access button will appear on the right side of your screen.
Choose How to Access Wiseone Features: Whether you prefer using the quick access button or the extension menu, Wiseone is always at your fingertips.
Start Exploring: Visit any webpage and unleash the power of Wiseone, whether searching for information or enhancing your online reading experience.
The Future of Digital Media Literacy
As we look to the future, it's evident that digital media will evolve at an unprecedented pace. New technologies, platforms, and communication methods will emerge, bringing fresh challenges and opportunities.
In this dynamic environment, the need for continuous improvement in digital media literacy becomes even more pronounced; it should not be viewed as a static skillset but as an opportunity for growth, remaining agile in critically assessing and engaging with online content.
Fostering digital media literacy skills has immeasurable long-term benefits. These skills enable individuals to navigate the complexities of the digital world and empower them to be active and informed.
A digitally literate person is more equipped to make informed decisions and engage in constructive dialogue.
Moreover, digital media literacy fosters a culture of lifelong learning and intellectual curiosity, invaluable in a world driven by information and innovation.
Enhance your web search,
Boost your reading productivity with Wiseone



